GraphRAG:用知识图谱增强RAG
RAG通过外挂知识库,适合LLM访问私人或者特定领域的数据并解决幻觉问题。
RAG的基本方法集成了向量数据库和LLM,其中向量数据库负责检索用户查询的上下文,LLM根据检索的上下文内容生成答案。这种方法在很多情况下效果好,速率快,但遇到复杂的问题就很难完成,譬如LLM的推理需要涉及不同的信息之间进行关联。
举一个例子,常规的RAG通常会按照下面的步骤来回答问题:
问题:识别这个人:确定谁打败了Allectus?
系统:
1、检索男人的儿子:查找此人家庭的信息,特别是他的儿子
2、LLM通过检索到的上下文找到儿子:识别儿子的名字
这里的挑战通常出现在检索环节,因为常规RAG基于语义相似性检索文本,而不能直接回答知识库中可能没有明确提及具体细节的复杂查询。这种限制使得很难找到所需的确切信息,通常需要昂贵且不切实际的解决方案,例如手动创建Q&A对以进行频繁的查询。
为了应对这些挑战,微软研究公司推出了GraphRAG,这是一种全新的方法,通过知识图增强RAG检索和生成。在接下来的章节中,我们将解释GraphRAG引擎如何工作,以及如何使用Milvus矢量数据库运行它。
GraphRAG的工作原理
与常规RAG不同的是,GraphRAG通过结合知识图谱(KG)来增强RAG。知识图谱在上一篇文章中已经讲过,它是根据实体之间的关系存储和索引相关或者无关数据的数据结构。
GraphRAG Pipeline通常由两个基本过程组成:索引和查询
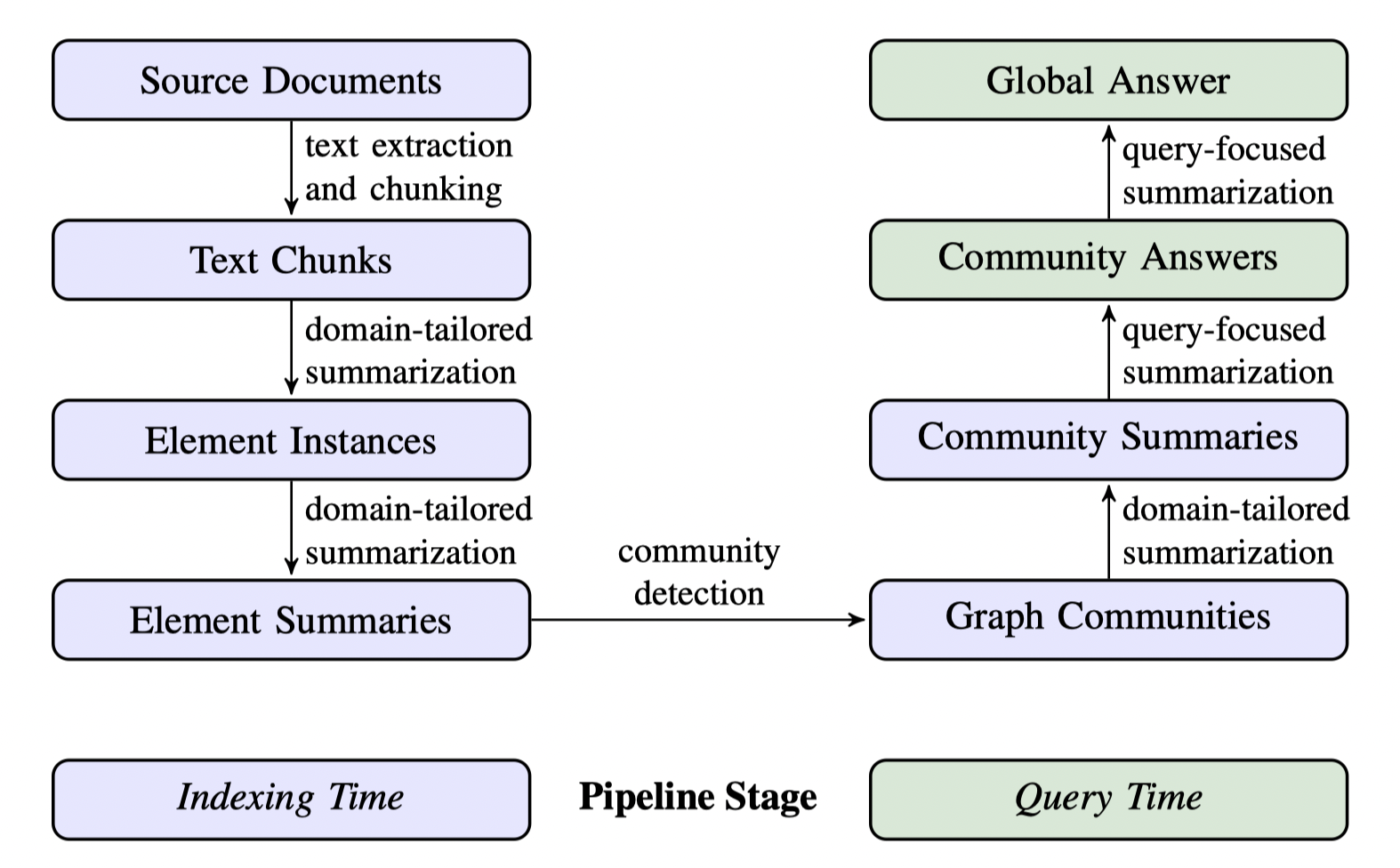
索引(Indexing)
GraphRAG的索引过程包括四个关键步骤:
1、文本单元分割(Chunking):整个输入语料库被划分为多个文本单元(文本块)。这些块是最小的可分析单位,可以是段落、句子或其他逻辑单位。通过将长文档分割成更小的块,我们可以提取和保存有关此输入数据的更多详细信息。
2、实体、关系和声明提取:GraphRAG使用LLM来识别和提取所有实体(人员、地点、组织等名称)、它们之间的关系以及每个文本单元文本中表达的关键声明。我们将使用这个提取的信息来构建一个初始知识图谱。
3、分层聚类:GraphRAG使用Leiden技术在初始知识图谱上执行分层聚类。Leiden是一种社区检索算法。可以有效发现图表中的社区结构。每个集群中的实体被分配给不同的社区,以便进行更深入的分析。
注意:社区是图中的一组节点,这些节点彼此紧密相连,但与网络中其他密集组的连接稀疏。
社区摘要生成:GraphRAG使用自下而上的方法为每个社区及其成员生成摘要。这些摘要包括社区内的主要实体、他们的关系和关键主张。此步骤概述了整个数据集,并为后续查询提供了有用的上下文信息。
提示词Tuning
尽管可以使用这里初始化的默认提示模板,但强烈建议通过GraphRAG提供的命令来创建自适应提示模板:GraphRAG会提取输入数据的信息,并借助大模型来分析与生成更具有针对性的提示模板。
提示词自适应调整的流程如下:
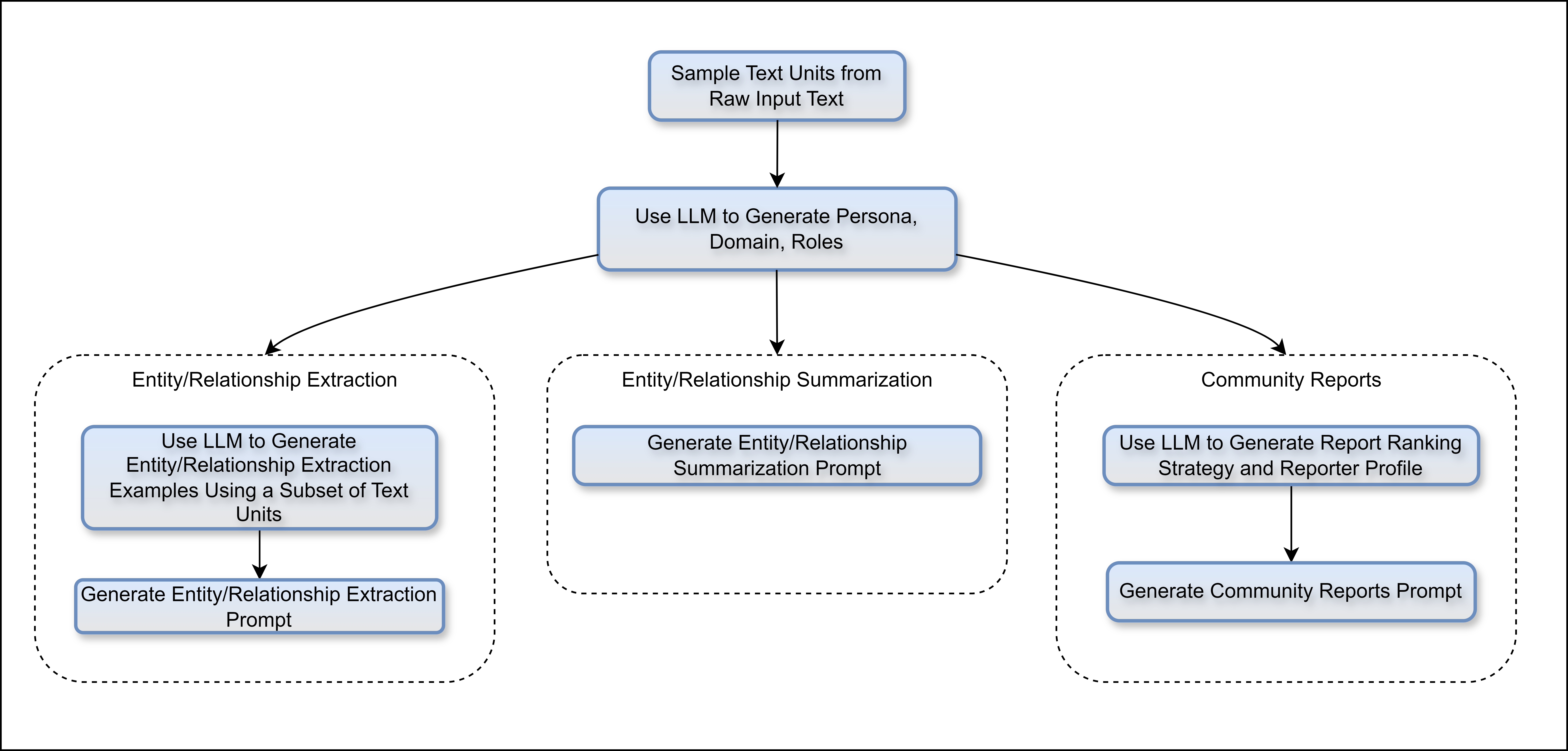
命令参数使用如下:
1
2
3
|
python -m graphrag.prompt_tune [--root ROOT] [--domain DOMAIN] [--method METHOD] [--limit LIMIT] [--language LANGUAGE] \
[--max-tokens MAX_TOKENS] [--chunk-size CHUNK_SIZE] [--n-subset-max N_SUBSET_MAX] [--k K] \
[--min-examples-required MIN_EXAMPLES_REQUIRED] [--no-entity-types] [--output OUTPUT]
|
参数说明:
--root(可选):数据项目根目录,包括配置文件(YML、JSON或.env)。默认为当前目录。--domain(可选):与您的输入数据相关的领域,如“空间科学”、“微生物学”或“环境新闻”。如果留空,域将从输入数据中推断出来。--method(可选):选择文档的方法。选项是全部、随机、自动或顶部。默认是随机的。--limit(可选):使用随机或顶部选择时加载的文本单位限制。默认值为15。如果大模型的token长度有限制,这里的limit参数可以设置小一些--language(可选):用于输入处理的语言。如果它与输入的语言不同,LLM将进行翻译。默认值为“”,这意味着它将从输入中自动检测到。--max-tokens(可选):提示生成的最大令牌数量。默认值为2000。需要注意这里的数值不包括输入的内容产生的token--chunk-size(可选):用于从输入文档生成文本单元的令牌大小。默认值为200。--n-subset-max(可选):使用自动选择方法时要嵌入的文本块chunk数量。默认值为300。--k(可选):使用自动选择方法时要选择的文档数量。默认值为15。--min-examples-required(可选):实体提取提示所需的最小示例数量。默认值为2。--no-entity-types(可选):使用未键入的实体提取生成。当您的数据涵盖许多主题或高度随机化时,我们建议使用此数据。--output(可选):保存生成提示的文件夹。默认值为“提示”。
使用8k长度的大模型,如下配置大概可以完整生成:python -m graphrag.prompt_tune --limit 10。
查询(Querying)
GraphRAG有两种不同的查询工作流程,专为不同的查询量身定做。
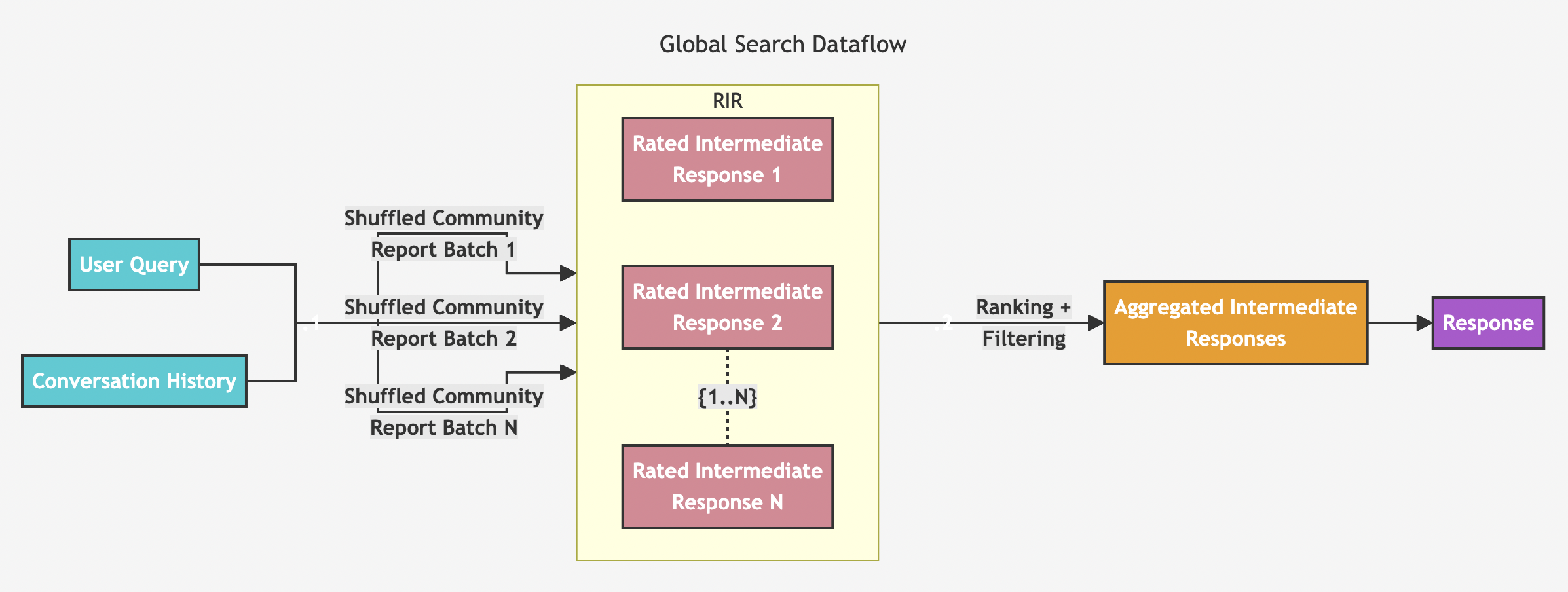
Global Search
Global Search工作流程包含以下阶段:
1、用户查询和对话历史记录:系统将用户查询和对话历史记录作为初始输入。
2、社区报告批处理:系统使用LLM从社区层次结构的指定级别生成的节点报告作为上下文数据。这些社区报告被洗牌并区分为多个批次。
3、评级中间回复(Rated Intermediate Responses, RIR): 每批社区报告都会被进一步划分为预定义大小的文本块。每个文本块用于生成一个中间回复。回复包含一个信息片段列表,称为点。每个点都有一个表示其重要性的数字分数。这些生成的中间回复就是额定中间回复(额定中间回复 1、回复 2……回复 N)。
4、排序和筛选:系统对这些中间回复进行排序和筛选,选出最重要的点。被选中的重要内容构成汇总的中间回复。
5、最终响应:聚合的中间响应被用作生成最终响应的上下文。
DeepSeekV2 翻译的中文版本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
# Copyright (c) 2024 Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License
"""全局搜索的系统提示词。"""
MAP_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---角色---
您是一个有帮助的助手,负责回答有关提供表格中数据的问题。
---目标---
生成一个包含关键点的响应,总结输入数据表格中所有相关信息,以回答用户的问题。
您应使用下面提供的数据表格中的数据作为生成响应的主要上下文。如果您不知道答案,或者输入数据表格不包含提供答案的足够信息,请直接说明。不要编造任何内容。
响应中的每个关键点应包含以下元素:
- 描述:对要点的全面描述。
- 重要性评分:一个介于0-100之间的整数评分,表示该要点在回答用户问题中的重要性。“我不知道”类型的响应应得分为0。
响应应以JSON格式如下:
{
"points": [
{"description": "要点1的描述 [数据来源:报告(报告ID)]", "score": 评分值},
{"description": "要点2的描述 [数据来源:报告(报告ID)]", "score": 评分值}
]
}
响应应保留原始含义和情态动词的使用,如“应”、“可能”或“将”。
支持数据的要点应列出相关报告作为参考,如下所示:
“这是一个由数据支持的示例句子 [数据来源:报告(报告ID)]”
**每个参考中不要列出超过5个记录ID**。相反,列出最相关的5个记录ID,并添加“+更多”以表示还有更多。
例如:
“Person X是Company Y的所有者,并且受到许多不当行为的指控 [数据来源:报告(2, 7, 64, 46, 34, +更多)]。他还是公司X的CEO [数据来源:报告(1, 3)]”
其中1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, 和64表示提供表格中相关数据报告的ID(非索引)。
不要包含没有提供支持证据的信息。
---数据表格---
{context_data}
---目标---
生成一个包含关键点的响应,总结输入数据表格中所有相关信息,以回答用户的问题。
您应使用下面提供的数据表格中的数据作为生成响应的主要上下文。如果您不知道答案,或者输入数据表格不包含提供答案的足够信息,请直接说明。不要编造任何内容。
每个关键点应包含以下元素:
- 描述:对要点的全面描述。
- 重要性评分:一个介于0-100之间的整数评分,表示该要点在回答用户问题中的重要性。“我不知道”类型的响应应得分为0。
响应应保留原始含义和情态动词的使用,如“应”、“可能”或“将”。
支持数据的要点应列出相关报告作为参考,如下所示:
“这是一个由数据支持的示例句子 [数据来源:报告(报告ID)]”
**每个参考中不要列出超过5个记录ID**。相反,列出最相关的5个记录ID,并添加“+更多”以表示还有更多。
例如:
“Person X是Company Y的所有者,并且受到许多不当行为的指控 [数据来源:报告(2, 7, 64, 46, 34, +更多)]。他还是公司X的CEO [数据来源:报告(1, 3)]”
其中1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, 和64表示提供表格中相关数据报告的ID(非索引)。
不要包含没有提供支持证据的信息。
响应应以JSON格式如下:
{
"points": [
{"description": "要点1的描述 [数据来源:报告(报告ID)]", "score": 评分值},
{"description": "要点2的描述 [数据来源:报告(报告ID)]", "score": 评分值}
]
}
"""
|
DeepSeekV2 翻译的中文版本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
# Copyright (c) 2024 Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License
"""全局搜索系统提示词。"""
REDUCE_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---角色---
您是一个有帮助的助手,负责通过综合多位分析师的观点来回答有关数据集的问题。
---目标---
生成一个符合目标长度和格式的响应,总结来自专注于数据集不同部分的多个分析师的报告,以回答用户的问题。
请注意,下面提供的分析师报告按**重要性降序排列**。
如果您不知道答案,或者提供的报告不包含提供答案的足够信息,请直接说明。不要编造任何内容。
最终响应应从分析师报告中移除所有无关信息,并将清理后的信息合并为一个全面的答案,该答案提供所有关键点和适当响应长度和格式的解释。
根据响应长度和格式的需要,添加适当的章节和评论。使用Markdown格式化响应。
响应应保留原始含义和情态动词的使用,如“应”、“可能”或“将”。
响应还应保留分析师报告中先前包含的所有数据参考,但在分析过程中不要提及多位分析师的角色。
**每个参考中不要列出超过5个记录ID**。相反,列出最相关的5个记录ID,并添加“+更多”以表示还有更多。
例如:
“Person X是Company Y的所有者,并且受到许多不当行为的指控 [数据来源:报告(2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +更多)]。他还是公司X的CEO [数据来源:报告(1, 3)]”
其中1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, 和64表示相关数据记录的ID(非索引)。
不要包含没有提供支持证据的信息。
---目标响应长度和格式---
{response_type}
---分析师报告---
{report_data}
---目标---
生成一个符合目标长度和格式的响应,总结来自专注于数据集不同部分的多个分析师的报告,以回答用户的问题。
请注意,下面提供的分析师报告按**重要性降序排列**。
如果您不知道答案,或者提供的报告不包含提供答案的足够信息,请直接说明。不要编造任何内容。
最终响应应从分析师报告中移除所有无关信息,并将清理后的信息合并为一个全面的答案,该答案提供所有关键点和适当响应长度和格式的解释。
响应应保留原始含义和情态动词的使用,如“应”、“可能”或“将”。
响应还应保留分析师报告中先前包含的所有数据参考,但在分析过程中不要提及多位分析师的角色。
**每个参考中不要列出超过5个记录ID**。相反,列出最相关的5个记录ID,并添加“+更多”以表示还有更多。
例如:
“Person X是Company Y的所有者,并且受到许多不当行为的指控 [数据来源:报告(2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +更多)]。他还是公司X的CEO [数据来源:报告(1, 3)]”
其中1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, 和64表示相关数据记录的ID(非索引)。
不要包含没有提供支持证据的信息。
---目标响应长度和格式---
{response_type}
根据响应长度和格式的需要,添加适当的章节和评论。使用Markdown格式化响应。
"""
NO_DATA_ANSWER = (
"很抱歉,由于提供的数据,我无法回答这个问题。"
)
GENERAL_KNOWLEDGE_INSTRUCTION = """
响应还可以包括数据集之外的相关现实世界知识,但必须明确标注验证标签 [LLM: 验证]。例如:
“这是一个由现实世界知识支持的示例句子 [LLM: 验证]。”
"""
|
MAP阶段的核心在于从原始数据中提取和整理信息,为后续的汇总和分析做准备,REDUCE阶段的核心在于整合和汇总多个分析师的报告来回答关于数据集的问题。简而言之,MAP阶段是数据处理的初步阶段,而REDUCE阶段是数据处理的最终汇总阶段。两者结合,形成了一个完整的数据分析和响应生成流程。
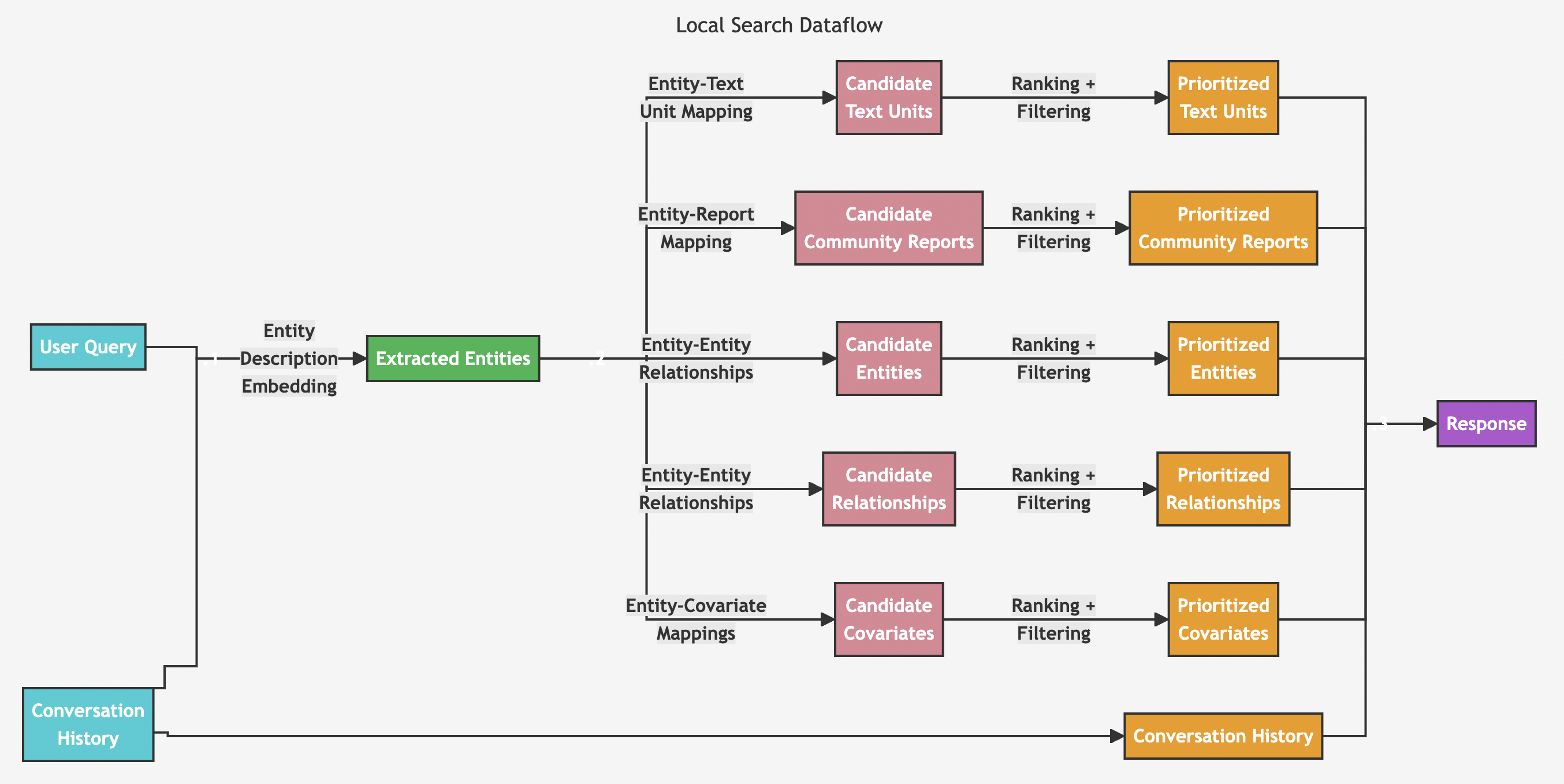
Local search
当用户直接询问有关特定实体(如人名、地点、组织等)的问题是,可以直接使用本地搜索工作流程。
Local Search工作流程包含以下阶段:
1、用户查询:首先,系统接收用户查询,这可能是一个简单的问题,也可以是更复杂的查询。
2、相似实体搜索:系统从知识图谱中识别出一组与用户输入语义相关的实体。这些实体是进入知识图谱的入口。这一步使用Milvus等向量数据库进行文本相似性搜索。
3、实体-文本单元映射(Entity-Text Unit Mapping):将提取的文本单元映射到相应的实体,去除原始文本信息。
4、实体关系提取(Entity-Relationship Extraction):该步骤提取有关实体及其相应关系的具体信息。
5、实体-协变量映射(Entity-Covariate Mapping):该步骤将实体映射到其协变量,其中可能包括统计数据或其他相关属性。
6、实体-社区报告映射(Entity-Community Report Mapping):将社区报告整合到搜索结果中,并纳入一些全局信息。
7、对话历史记录的利用:如果提供,系统将使用对话历史记录来更好地了解用户的意图和上下文。
8、生成回复:最后,系统根据前面步骤中生成的经过筛选和排序的数据构建并回复用户查询。
DeepSeekV2 翻译的中文版本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
# Copyright (c) 2024 Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License
"""本地搜索系统提示词。"""
LOCAL_SEARCH_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---角色---
您是一个有帮助的助手,负责回答有关提供表格中数据的问题。
---目标---
生成一个符合目标长度和格式的响应,总结输入数据表格中所有信息,以回答用户的问题,并结合任何相关的常识知识。
如果您不知道答案,请直接说明。不要编造任何内容。
支持数据的要点应列出其数据参考,如下所示:
“这是一个由多个数据参考支持的示例句子 [数据来源:<数据集名称>(记录ID);<数据集名称>(记录ID)]。”
每个参考中不要列出超过5个记录ID。相反,列出最相关的5个记录ID,并添加“+更多”以表示还有更多。
例如:
“Person X是Company Y的所有者,并且受到许多不当行为的指控 [数据来源:来源(15, 16),报告(1),实体(5, 7);关系(23);索赔(2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +更多)]。”
其中15, 16, 1, 5, 7, 23, 2, 7, 34, 46, 和64表示相关数据记录的ID(非索引)。
不要包含没有提供支持证据的信息。
---目标响应长度和格式---
{response_type}
---数据表格---
{context_data}
---目标---
生成一个符合目标长度和格式的响应,总结输入数据表格中所有信息,以回答用户的问题,并结合任何相关的常识知识。
如果您不知道答案,请直接说明。不要编造任何内容。
支持数据的要点应列出其数据参考,如下所示:
“这是一个由多个数据参考支持的示例句子 [数据来源:<数据集名称>(记录ID);<数据集名称>(记录ID)]。”
每个参考中不要列出超过5个记录ID。相反,列出最相关的5个记录ID,并添加“+更多”以表示还有更多。
例如:
“Person X是Company Y的所有者,并且受到许多不当行为的指控 [数据来源:来源(15, 16),报告(1),实体(5, 7);关系(23);索赔(2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +更多)]。”
其中15, 16, 1, 5, 7, 23, 2, 7, 34, 46, 和64表示相关数据记录的ID(非索引)。
不要包含没有提供支持证据的信息。
---目标响应长度和格式---
{response_type}
根据响应长度和格式的需要,添加适当的章节和评论。使用Markdown格式化响应。
"""
|
整体上看GraphRAG与LLM的交互非常频繁,流程也较为复杂,将这些不同的流程抽象出来,可以总结为以下流程图:
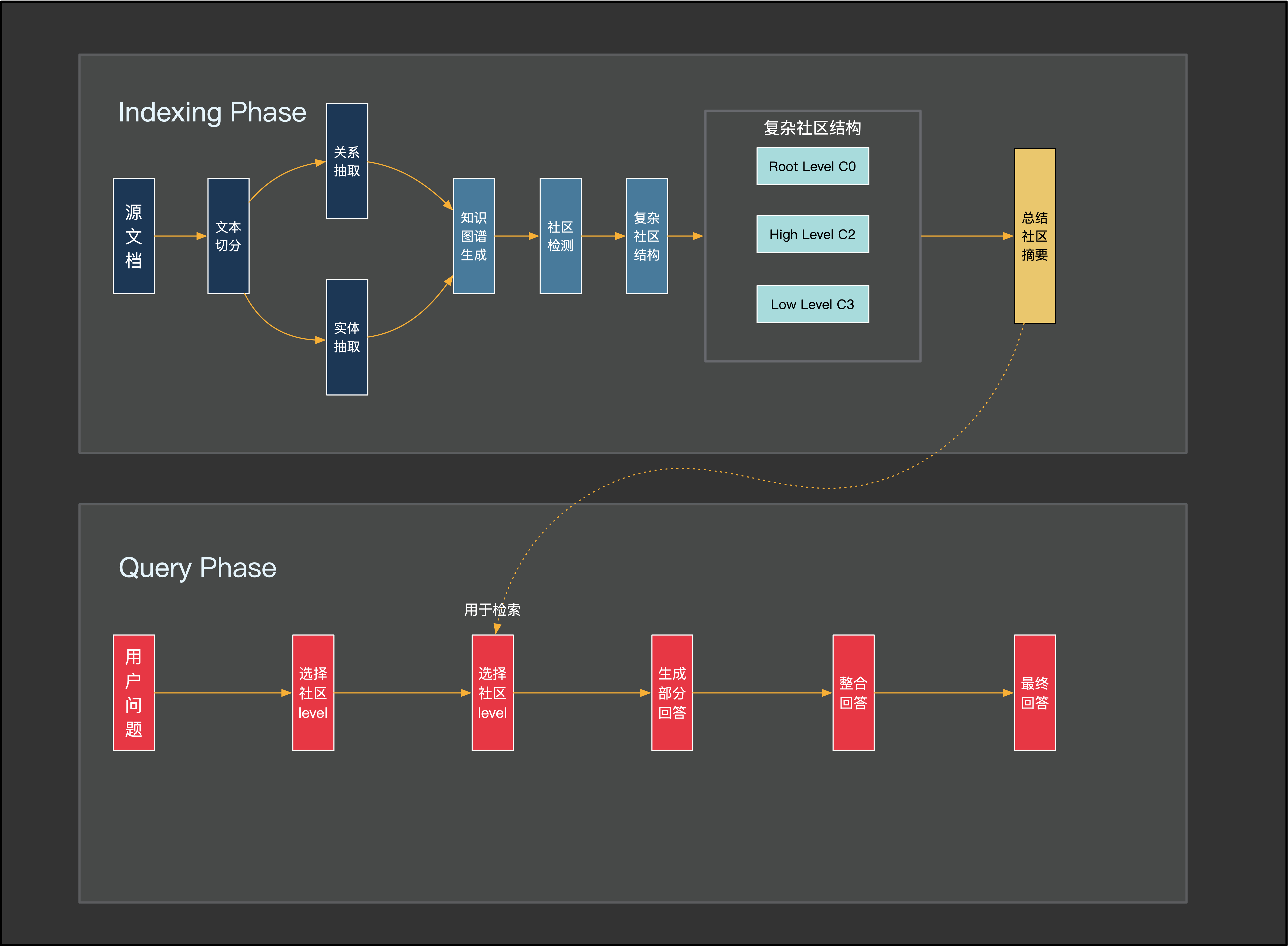
Reference:
1、From Local to Global: A Graph RAG Approach to Query-Focused Summarization: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.16130
2、GraphRAG Documents: https://microsoft.github.io/graphrag
GraphRAG实操
这里直接使用conda来管理graphrag的项目环境。
1
2
3
|
conda create -n graphrag python=3.11
conda activate graphrag
pip install graphrag
|
1
2
3
|
mkdir graphrag
cd graphrag
python -m graphrag.index --init --root .
|
初始化成功之后,目录会多出下面这些文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
├── prompts
│ ├── claim_extraction.txt
│ ├── community_report.txt
│ ├── entity_extraction.txt
│ ├── summarize_descriptions.txt
├── .env
└── settings.yaml
|
其中prompts文件夹是GraphRAG使用到的LLM提示词,.env中保存LLM和embedding模型的api-key信息。
如果你使用闭源模型,可以使用默认设置,设置好api-key就可以了。
如果你使用本地openai格式的模型,需要改变一些设置。本人使用的是qwen1.5-32b-chat-gptq-int4和bge-base-en-v1.5,settings.yaml的内容如下(参考):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
|
encoding_model: cl100k_base
skip_workflows: []
llm:
api_key: ${GRAPHRAG_API_KEY}
type: openai_chat # or azure_openai_chat
model: qwen2-72b-instruct-gptq-int4
model_supports_json: true # recommended if this is available for your model.
max_tokens: 8192
# request_timeout: 180.0
api_base: http://localhost:3000/v1
# api_version: 2024-02-15-preview
# organization: <organization_id>
# deployment_name: <azure_model_deployment_name>
# tokens_per_minute: 150_000 # set a leaky bucket throttle
# requests_per_minute: 10_000 # set a leaky bucket throttle
# max_retries: 10
# max_retry_wait: 10.0
# sleep_on_rate_limit_recommendation: true # whether to sleep when azure suggests wait-times
# concurrent_requests: 25 # the number of parallel inflight requests that may be made
# temperature: 0 # temperature for sampling
# top_p: 1 # top-p sampling
# n: 1 # Number of completions to generate
parallelization:
stagger: 0.3
# num_threads: 50 # the number of threads to use for parallel processing
async_mode: threaded # or asyncio
embeddings:
## parallelization: override the global parallelization settings for embeddings
async_mode: threaded # or asyncio
# target: required # or all
llm:
api_key: ${GRAPHRAG_API_KEY}
type: openai_embedding # or azure_openai_embedding
model: bge-base-en-v1.5
api_base: http://localhost:8000/v1
# api_version: 2024-02-15-preview
# organization: <organization_id>
# deployment_name: <azure_model_deployment_name>
# tokens_per_minute: 150_000 # set a leaky bucket throttle
# requests_per_minute: 10_000 # set a leaky bucket throttle
# max_retries: 10
# max_retry_wait: 10.0
# sleep_on_rate_limit_recommendation: true # whether to sleep when azure suggests wait-times
# concurrent_requests: 25 # the number of parallel inflight requests that may be made
# batch_size: 16 # the number of documents to send in a single request
# batch_max_tokens: 8191 # the maximum number of tokens to send in a single request
chunks:
size: 400
overlap: 100
group_by_columns: [id] # by default, we don't allow chunks to cross documents
input:
type: file # or blob
file_type: text # or csv
base_dir: "input"
file_encoding: utf-8
file_pattern: ".*\\.md$"
cache:
type: file # or blob
base_dir: "cache"
# connection_string: <azure_blob_storage_connection_string>
# container_name: <azure_blob_storage_container_name>
storage:
type: file # or blob
base_dir: "output/${timestamp}/artifacts"
# connection_string: <azure_blob_storage_connection_string>
# container_name: <azure_blob_storage_container_name>
reporting:
type: file # or console, blob
base_dir: "output/${timestamp}/reports"
# connection_string: <azure_blob_storage_connection_string>
# container_name: <azure_blob_storage_container_name>
entity_extraction:
## llm: override the global llm settings for this task
## parallelization: override the global parallelization settings for this task
## async_mode: override the global async_mode settings for this task
prompt: "prompts/entity_extraction.txt"
entity_types: [organization,person,geo,event]
max_gleanings: 1
summarize_descriptions:
## llm: override the global llm settings for this task
## parallelization: override the global parallelization settings for this task
## async_mode: override the global async_mode settings for this task
prompt: "prompts/summarize_descriptions.txt"
max_length: 500
claim_extraction:
## llm: override the global llm settings for this task
## parallelization: override the global parallelization settings for this task
## async_mode: override the global async_mode settings for this task
# enabled: true
prompt: "prompts/claim_extraction.txt"
description: "Any claims or facts that could be relevant to information discovery."
max_gleanings: 1
community_reports:
## llm: override the global llm settings for this task
## parallelization: override the global parallelization settings for this task
## async_mode: override the global async_mode settings for this task
prompt: "prompts/community_report.txt"
max_length: 2000
max_input_length: 8000
cluster_graph:
max_cluster_size: 10
embed_graph:
enabled: false # if true, will generate node2vec embeddings for nodes
# num_walks: 10
# walk_length: 40
# window_size: 2
# iterations: 3
# random_seed: 597832
umap:
enabled: false # if true, will generate UMAP embeddings for nodes
snapshots:
graphml: false
raw_entities: false
top_level_nodes: false
local_search:
# text_unit_prop: 0.5
# community_prop: 0.1
# conversation_history_max_turns: 5
# top_k_mapped_entities: 10
# top_k_relationships: 10
# llm_temperature: 0 # temperature for sampling
# llm_top_p: 1 # top-p sampling
# llm_n: 1 # Number of completions to generate
# max_tokens: 12000
global_search:
# llm_temperature: 0 # temperature for sampling
# llm_top_p: 1 # top-p sampling
# llm_n: 1 # Number of completions to generate
# max_tokens: 12000
# data_max_tokens: 12000
# map_max_tokens: 1000
# reduce_max_tokens: 2000
# concurrency: 32
|
主要的改动集中在LLM和embedding模型的地址和model_name以及知识库文档的类型(这里使用的.md),最后根据文档和回答的预期长度修改了chunk_size。
1
|
python -m graphrag.index --root .
|
等待很久很久之后。。。
1
|
python -m graphrag.query --root . --method global "What are the top themes in this paper?"
|
回答结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
The top themes in this paper center around the FastSegFormer models, their advancements in image segmentation, efficiency, and real-time capabilities. FastSegFormer-E and FastSegFormer-P are the primary models discussed, which leverage knowledge distillation to enhance their performance. This technique is crucial in transferring knowledge from a more complex 'teacher' network to the FastSegFormer models, thereby improving their accuracy [Data: Reports (9, 14, 10, 16)].
The paper also delves into comparative evaluations, where FastSegFormer is benchmarked against well-known models like Swin-T-Att-UNet, EfficientNet, and ENet, demonstrating its competitive performance in various tasks [Data: Reports (9, 14, 11)]. The practical applications of the models are showcased through evaluations on devices such as the GeForce RTX3060, highlighting their compatibility with contemporary hardware [Data: Reports (9, 14, 6)].
Ablation studies are conducted to understand the impact of specific components like the Image Refinement Block (IRB), Multi-Scale Prediction (MSP), and Pyramid Pooling Module (PPM), providing insights into the design choices and their contributions to the model's overall performance [Data: Reports (9, 14, 15)].
FastSegFormer models come in different variants, tailored for accuracy, memory efficiency, or speed, catering to diverse use cases [Data: Reports (14, 15)]. The role of CUDA and GeForce RTX3060 in facilitating model training and inference is also emphasized, underlining the importance of GPU technology in computer vision tasks [Data: Reports (0, 2)].
Lastly, the paper explores the application of FastSegFormer in semantic segmentation tasks, such as fruit defect detection and medical image segmentation, demonstrating its versatility in real-world scenarios [Data: Reports (7, 6)]. DS Conv Modules, an innovation in computer vision, are utilized in FastSegFormer for efficient decoding, further optimizing the model's performance [Data: Reports (2, 0)].
|
因为这篇论文是我自己写的,所以从我的角度出发,它的总结质量是很高的,和我自己总结是差不多的!
1
|
python -m graphrag.query --root . --method local "What are the common diseases of citrus? Which ones are studied in detail in this article?"
|
回答结果:
1
2
3
4
5
|
柑橘类水果常见的疾病包括黄龙病、溃疡病、疮痂病、煤烟病等。然而,提供的数据表格并没有直接列出所有柑橘类疾病的详细列表,而是集中在研究柑橘(特别是脐橙)的特定缺陷检测上,如风斑、溃疡和日灼。这些缺陷并不是传统意义上的植物疾病,而是水果在生长过程中可能遇到的表面问题,可能是由于环境因素(如风、太阳曝晒)或病害引起的。
文章详细研究了风斑(wind scarring)、溃疡(ulcers)和日灼(sunburn)这三种脐橙的表面缺陷,收集了1448张分辨率为2592 × 1944像素的图片用于训练和标记,然后使用图像处理和深水果质量的不断提升的需求。
因此,虽然柑橘类水果可能面临多种疾病挑战,但这篇文章主要关注的是作为水果缺陷的风斑、溃疡和日灼的检测技术,而不是对柑橘类植物疾病的广泛研究。
|
细节问题也是回答得比较准确,但是不知道为啥问的是英文,知识库也是英文的,回答得是中文,难道是因为用了Qwen系列模型的原因?
GraphRAG集成
在实际的项目中,我们需要的可能只是GraphRAG的部分组件,那么如何使用GraphRAG的相关的功能集成进入你自己的项目非常重要。
Local search
下面我将使用Milvus数据库和GraphRAG来完成本地功能。
- 环境准备,由于
Milvus还没有正式集成进入GraphRAG(9月2日),所以我们需要更新开发版本的GraphRAG。
1
2
|
pip install --upgrade pymilvus
pip install git+https://github.com/zc277584121/graphrag.git
|
- 按照上面的设置教程,删除cache,重新进行indexing:
1
2
|
rm -rf cache
python -m graphrag.index --root .
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
import os
import pandas as pd
import tiktoken
from graphrag.query.context_builder.entity_extraction import EntityVectorStoreKey
from graphrag.query.indexer_adapters import (
read_indexer_covariates,
read_indexer_entities,
read_indexer_relationships,
read_indexer_reports,
read_indexer_text_units,
)
from graphrag.query.input.loaders.dfs import (
store_entity_semantic_embeddings,
)
from graphrag.query.llm.oai.chat_openai import ChatOpenAI
from graphrag.query.llm.oai.embedding import OpenAIEmbedding
from graphrag.query.llm.oai.typing import OpenaiApiType
from graphrag.query.question_gen.local_gen import LocalQuestionGen
from graphrag.query.structured_search.local_search.mixed_context import (
LocalSearchMixedContext,
)
from graphrag.query.structured_search.local_search.search import LocalSearch
from graphrag.vector_stores import MilvusVectorStore
import asyncio
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
index_root = "./"
# 取到最后一次存储的结果
output_dir = os.path.join(index_root, "output")
subdirs = [os.path.join(output_dir, d) for d in os.listdir(output_dir)]
latest_subdir = max(subdirs, key=os.path.getmtime) # Get latest output directory
INPUT_DIR = os.path.join(latest_subdir, "artifacts")
COMMUNITY_REPORT_TABLE = "create_final_community_reports"
ENTITY_TABLE = "create_final_nodes"
ENTITY_EMBEDDING_TABLE = "create_final_entities"
RELATIONSHIP_TABLE = "create_final_relationships"
COVARIATE_TABLE = "create_final_covariates"
TEXT_UNIT_TABLE = "create_final_text_units"
COMMUNITY_LEVEL = 2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
# Read entities
entity_df = pd.read_parquet(f"{INPUT_DIR}/{ENTITY_TABLE}.parquet") # 读取实体表
entity_embedding_df = pd.read_parquet(f"{INPUT_DIR}/{ENTITY_EMBEDDING_TABLE}.parquet") # 读取实体embedding表
entities = read_indexer_entities(entity_df, entity_embedding_df, COMMUNITY_LEVEL)
description_embedding_store = MilvusVectorStore(
collection_name="entity_description_embeddings",
)
# description_embedding_store.connect(uri="http://localhost:19530") # For Milvus docker service
description_embedding_store.connect(uri="./milvus.db") # For Milvus Lite
# 存储Milvus向量
entity_description_embeddings = store_entity_semantic_embeddings(
entities=entities, vectorstore=description_embedding_store
)
print(f"Entity count: {len(entity_df)}")
print(entity_df.head()) # 打印前五行数据
# Entity count: 674
# level title ... x y
# 0 0 FASTSEGFOMER ... 0 0
# 1 0 NAVEL ORANGE ... 0 0
# 2 0 DEFECT DETECTION ... 0 0
# 3 0 SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION ... 0 0
# 4 0 ENET ... 0 0
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
# Read relationships
relationship_df = pd.read_parquet(f"{INPUT_DIR}/{RELATIONSHIP_TABLE}.parquet")
relationships = read_indexer_relationships(relationship_df)
print(f"Relationship count: {len(relationship_df)}")
print(relationship_df.head()) # 打印前五行数据
# Relationship count: 146
# source target ... target_degree rank
# 0 FASTSEGFOMER FASTSEGFOMER-E ... 2 4
# 1 FASTSEGFOMER FASTSEGFOMER-P ... 2 4
# 2 DEFECT DETECTION REAL-TIME DETECTION ... 1 3
# 3 DEFECT DETECTION PROMPT ENGINEERING ... 1 3
# 4 ENET FASTSEGFOMER-E ... 2 6
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# Read community reports
report_df = pd.read_parquet(f"{INPUT_DIR}/{COMMUNITY_REPORT_TABLE}.parquet")
reports = read_indexer_reports(report_df, entity_df, COMMUNITY_LEVEL)
print(f"Report records: {len(report_df)}")
print(report_df.head()) # 打印前五行数据
# Report records: 3
# community ... id
# 0 3 ... d4b5a9ec-7256-455f-9f2a-518310609dc9
# 1 4 ... 42b3362d-7e9d-4d96-a60d-6b8fa0245c81
# 2 2 ... 83e2a318-8e0d-4816-97ad-ed1ff641c0c5
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
# Read text units
text_unit_df = pd.read_parquet(f"{INPUT_DIR}/{TEXT_UNIT_TABLE}.parquet")
text_units = read_indexer_text_units(text_unit_df)
print(f"Text unit records: {len(text_unit_df)}")
print(text_unit_df.head()) # 打印前五行数据
# Text unit records: 82
# id ... relationship_ids
# 0 c96b41feb79908fce97190106d611335 ... [f2c06f3a0c704296bf3353b91ee8af47, f512103ed46...
# 1 a0c9245bdb541e615779f3e1833bdeeb ... [ef00ec3a324f4f5986141401002af3f6, 4d183e70076...
# 2 6b24ab6355490e05891aada3810a2ae2 ... [24652fab20d84381b112b8491de2887e, d4602d4a27b...
# 3 2e37b6df0cc9e287ed8a46fc169f1f67 ... [2325dafe50d1435cbee8ebcaa69688df, ad52ba79a84...
# 4 6129ec8b3c26cf9ad8a6dc6501afa6e5 ... [bdddcb17ba6c408599dd395ce64f960a, bc70fee2061...
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
llm = ChatOpenAI(
api_key="<your_api_key>",
api_base="<your_api_base>",
model="<your_model_name>",
api_type=OpenaiApiType.OpenAI,
max_retries=20,
)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
# Create local search
context_builder = LocalSearchMixedContext(
community_reports=reports,
text_units=text_units,
entities=entities,
relationships=relationships,
covariates=None, #covariates,#todo
entity_text_embeddings=description_embedding_store,
embedding_vectorstore_key=EntityVectorStoreKey.ID, # if the vectorstore uses entity title as ids, set this to EntityVectorStoreKey.TITLE
text_embedder=text_embedder,
token_encoder=token_encoder,
)
|
- 设置local搜索的上下文相关参数和大模型相关的参数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
local_context_params = {
"text_unit_prop": 0.5,
"community_prop": 0.1,
"conversation_history_max_turns": 5,
"conversation_history_user_turns_only": True,
"top_k_mapped_entities": 10,
"top_k_relationships": 10,
"include_entity_rank": True,
"include_relationship_weight": True,
"include_community_rank": False,
"return_candidate_context": False,
"embedding_vectorstore_key": EntityVectorStoreKey.ID, # set this to EntityVectorStoreKey.TITLE if the vectorstore uses entity title as ids
"max_tokens": 5000, # 根据您模型上的令牌限制进行更改(如果您使用的是具有8k限制的模型,良好的设置可能是5000)
}
llm_params = {
"max_tokens": 1000, # 根据模型上的令牌限制进行更改(如果您使用的是8k限制的模型,一个好的设置可能是1000~1500)
"temperature": 0.0,
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
search_engine = LocalSearch(
llm=llm,
context_builder=context_builder,
token_encoder=token_encoder,
llm_params=llm_params,
context_builder_params=local_context_params,
response_type="multiple paragraphs", # 描述响应类型和格式的自由格式文本,可以是任何东西,例如优先列表、单段、多段、多页报告 (这里是通过大模型提示词的方式输入,所以可以自由发挥)
)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
async def local_search(query, engine):
result = await engine.asearch(query, history=None)
print(result.response)
asyncio.run(local_search("What are the common diseases of citrus? Which ones are studied in detail in this article?", search_engine))
# 柑橘类水果,如脐橙,常会受到多种疾病的困扰,这些疾病可能影响果实的生长和运输,导致外观缺陷和品质下降。然而,具体到柑橘类的常见疾病,如黄龙病、柑橘溃疡病、疮痂病等,本文并未详细列举。文章的焦点集中在脐橙的缺陷检测上,利用深度学习,特别是语义分割技术,来提升水果缺陷分类的准确性和效率。文章提出的FastSegFormer网络,结合了多尺度金字塔(MSP)模块和半分辨率重建分支,用于实时柑橘缺陷检测。文章中并未深入探讨具体的柑橘疾病,而是集中于如何通过FastSegFormer网络来改进对这些疾病导致的果实缺陷的识别能力。因此,对于柑橘类的常见疾病及其详细研究,本文并不提供相关信息。
|
问题总结
GraphRAG还可以根据历史查询生成问题,这对于在聊天机器人对话框中创建推荐问题很有用。该方法将知识图中的结构化数据与输入文档中的非结构化数据相结合,以生成与特定实体相关的候选问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
question_generator = LocalQuestionGen(
llm=llm,
context_builder=context_builder,
token_encoder=token_encoder,
llm_params=llm_params,
context_builder_params=local_context_params,
)
question_history = [
"Tell me what is knowledge distillation method",
"What knowledge distillation methods are used in this article?",
]
async def question_gen(query_history, context_data):
candidate_questions = await question_generator.agenerate(
question_history=query_history, context_data=context_data, question_count=5
)
return candidate_questions.response
async def local_search(query, engine):
result = await engine.asearch(query, history=None)
print(result.response)
# 为了查看问题生成的效果,我们进行了对比实验!
print("=========Local search=========")
print()
asyncio.run(local_search("Tell me what is knowledge distillation method. What knowledge distillation methods are used in this article?", search_engine))
print()
print("=========Local search with question generation=========")
print()
new_query_list = asyncio.run(question_gen(question_history, None))
for new_query in new_query_list:
print(f"New query: {new_query}")
asyncio.run(local_search(new_query, search_engine))
|
结果如下(因为回答的格式本身是markdown,直接使用html渲染了,公式也写对了,信息基本无误,回答质量不同):
=========Local search=========
Knowledge distillation is a machine learning technique where a smaller, more efficient model (called the student model) learns from a larger, more complex model (called the teacher model) to improve its performance. This process typically involves the transfer of knowledge from the teacher’s predictions or internal representations to the student, allowing the student to mimic the teacher’s behavior while requiring fewer resources. The main goal of knowledge distillation is to compress the knowledge of a large model into a smaller one without sacrificing too much accuracy.
In the context of the article, knowledge distillation is employed to enhance the performance of the proposed FastSegFormer models, FastSegFormer-P and FastSegFormer-E. Two knowledge distillation methods are mentioned:
-
Knowledge Distillation from T-224 (KD1): This method involves using a teacher model with a 224x224 input size to guide the learning of the student model. The teacher model’s predictions are used as soft targets to train the student, allowing it to learn from the richer information provided by the teacher’s softened probabilities.
-
Knowledge Distillation from T-512 (KD2): This method is similar to KD1, but it uses a teacher model with a larger 512x512 input size. The larger input size typically captures more detailed information, which can be beneficial for the student model’s learning process.
The article reports the results of these knowledge distillation methods on the FastSegFormer-P model, demonstrating improved segmentation performance compared to the model without distillation. The use of knowledge distillation is a key aspect of the study, as it allows the development of more efficient models that maintain high accuracy, which is particularly important in resource-constrained environments like edge computing devices for real-time fruit defect detection.
=========Local search with question generation=========
New query: - Which methods are employed for knowledge distillation in the context of the SIMPLE NETWORK and the complex model?
Knowledge distillation is a technique used to transfer the knowledge learned by a complex model, often referred to as the teacher model, to a simpler model, known as the student model. In the context of the SIMPLE NETWORK and the complex model, the distillation process involves multiple components. The primary loss function includes three parts: cross-entropy loss, logits distillation loss, and a feature distillation loss based on normalized feature differences (NFD). The cross-entropy loss measures the difference between the predicted outputs of the student model and the ground truth labels. The logits distillation loss aligns the output probabilities of the teacher and student models, while the feature distillation loss encourages the student model to mimic the intermediate feature representations of the teacher model.
The feature distillation loss is calculated using the Euclidean distance between the normalized feature maps of the teacher and student networks. Normalization is applied to the feature maps to ensure a fair comparison. The equation for normalization is given as:
$${\bar{F}}={\frac{1}{\sigma}}(F-u)$$
where $\bar{F}$ represents the normalized feature map, $F$ is the original feature map, $\sigma$ is the standard deviation, and $u$ is the mean of the features.
The total loss function is a weighted sum of these three components, with $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$ as the weighting coefficients for logits distillation loss and feature distillation loss, respectively. In the specific case mentioned, $\lambda_1$ is set to 0.5 and $\lambda_2$ is set to 5, ensuring that the feature distillation loss and logits distillation loss contribute comparably to the overall training process.
This knowledge distillation strategy is designed to enhance the performance of the simpler student model without increasing its size or inference time, making it more efficient and suitable for deployment in resource-constrained environments. By leveraging the knowledge from a more powerful teacher model, the student model can achieve improved accuracy in tasks such as image segmentation, as demonstrated in the context of FastSegFormer models for fruit defect detection.
可以明显地看到提升,不再是原本的笼统的说法,而本文使用的蒸馏方法由哪几部分组成,以及部分蒸馏损失的核心思想公式。
1
2
3
|
import shutil
shutil.rmtree("your_kg_result_dir")
|
Neo4j + GraphRAG
GraphRAG生成的数据文件是以parquet文件的形式存储的,我们可以将这些文件导入到图形数据库Neo4j中,一般方法是通过CSV文件导入并构建知识图谱,通过转化文件手动导入的教程可以参考国外一篇博客的内容:🔗click。
当然也可以参考另外一个转化教程:🔗click
较新的neo4j数据库需要java jdk17/20的支持,需要下载较新的版本!本地部署:
1
2
3
4
|
curl -O https://dist.neo4j.org/neo4j-community-5.23.0-unix.tar.gz
cd neo4j-community-5.23.0
./bin/neo4j start
./bin/neo4j status
|
图形检索器
在进入检索器实现之前,我们将进行一个简单的图形分析,以熟悉提取的数据。我们首先定义数据库连接和执行Cypher语句(图形数据库查询语言)并输出Pandas DataFrame的函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import pandas as pd
NEO4J_URI="bolt://localhost"
NEO4J_USERNAME="neo4j"
NEO4J_PASSWORD="password"
driver = GraphDatabase.driver(NEO4J_URI, auth=(NEO4J_USERNAME, NEO4J_PASSWORD))
def db_query(cypher: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = {}) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Executes a Cypher statement and returns a DataFrame"""
return driver.execute_query(
cypher, parameters_=params, result_transformer_=Result.to_df
)
|
执行图形提取,默认使用的chunk大小为300。我们可以使用以下Cypher语句来验证块大小。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
db_query(
"MATCH (n:__Chunk__) RETURN n.n_tokens as token_count, count(*) AS count"
)
# token_count count
# 300 15
# 155 1
|
存在15个300token的chunks,最后一个仅有155个token
接下来,我们将要配置检索器来集成Neo4j图形数据库!
在全局检索中,必须提前决定哪个定义了我们想要迭代的层次,等级级别越高,社区就越大,但社区越少。我们将使用LangChain实现全局检索器,使用相同的map,并减少与GraphRAG论文中的提示词。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
def global_retriever(query: str, level: int, response_type: str = response_type) -> str:
community_data = graph.query(
"""
MATCH (c:__Community__)
WHERE c.level = $level
RETURN c.full_content AS output
""",
params={"level": level},
)
intermediate_results = []
for community in tqdm(community_data, desc="Processing communities"):
intermediate_response = map_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "context_data": community["output"]}
)
intermediate_results.append(intermediate_response)
final_response = reduce_chain.invoke(
{
"report_data": intermediate_results,
"question": query,
"response_type": response_type,
}
)
return final_response
|
完整的代码请参考:🔗click
其他替代方案(Triplex)
微软使用的是GPT-4O这种超级大模型进行实体和关系抽取,替代的方案则是对实体抽取专门使用了一个较小的LLM叫SciPhi/Triplex来进行实体和关系的抽取,它实际上是一个经过微调的大语言模型,但是参数量更小。
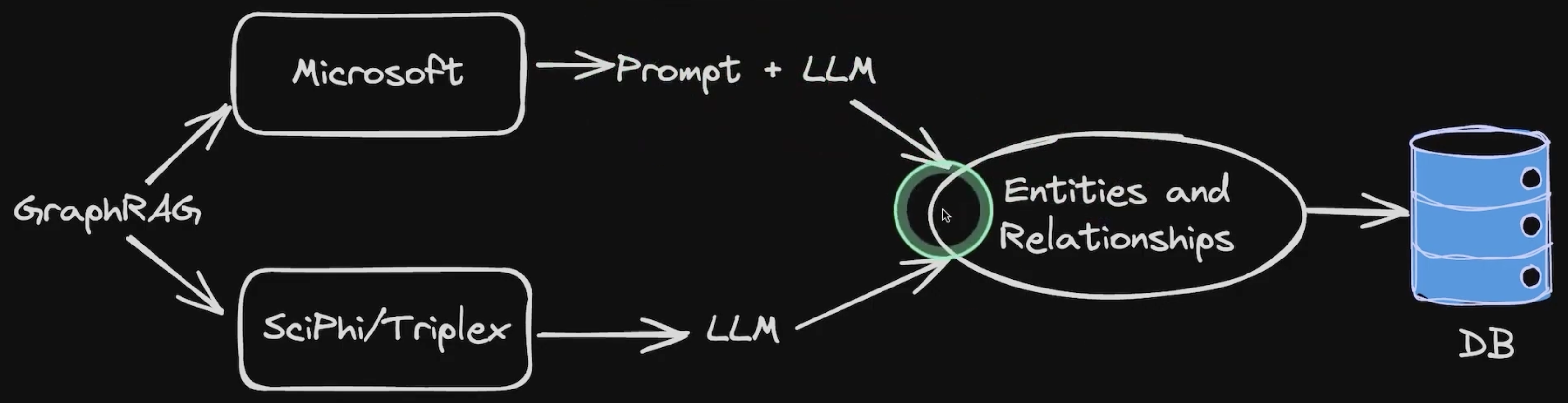
Triplex模型如下:🔗click,Triplex是Phi3-3.8B的微调版本,用于从SciPhi.AI开发的非结构化数据中创建知识图。它的工作原理是从文本或其他数据源中提取三元组——由主语、谓语和宾语组成的简单语句。
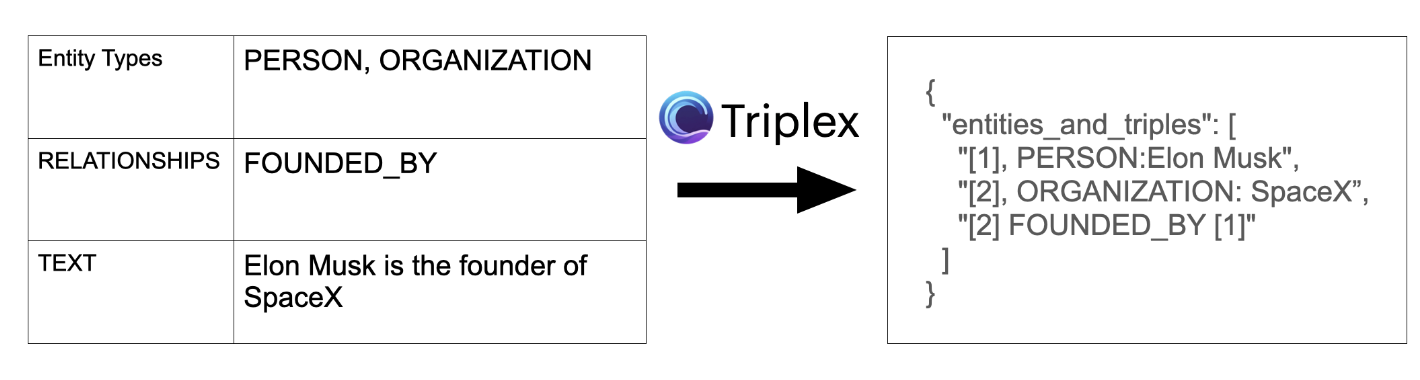
目前这种技术已经在R2R工具中集成了,它可以使用ollama使用triplex模型 + 用于回答的LLM + 用于嵌入的embedding模型来使用GraphRAG。具体使用方法:🔗click
总结
在拥有本地大模型(32B以上)的情况下,GraphRAG的成本会有所下降,顶多就是多点电费,随着大模型的基础能力越来越强,GraphRAG的使用成本会越来越低,这种通过实体关系来搜索的方式加强了不同文档之间的联系。
最后修改于 2024-09-02

本作品采用
知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。







