1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
|
import math
import cv2 as cv
import openpyxl
#图像二值化
'''
使用自适应阈值分割:
它的思想不是计算全局图像的阈值,而是根据图像不同区域亮度分布,计算其局部阈值,所以对于图像不同区域,能够自适应计算不同的阈值,因此被称为自适应阈值法。
如何确定局部阈值呢?可以计算某个邻域(局部)的均值、中值、高斯加权平均(高斯滤波)来确定阈值。
cv2.adaptiveThreshold(src, maxValue, adaptiveMethod, thresholdType, blockSize, C, dst=None)
src:灰度化的图片
maxValue:满足条件的像素点需要设置的灰度值
adaptiveMethod:自适应方法。有2种:ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C 或 ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C(均值和高斯)
thresholdType:二值化方法,可以设置为THRESH_BINARY或者THRESH_BINARY_INV (大于阈值部分取maxval,否则取0);另一个为反向
blockSize:分割计算的区域大小,取奇数
C:常数,每个区域计算出的阈值的基础上在减去这个常数作为这个区域的最终阈值,可以为负数
dst:输出图像,可选
'''
def binary_img(img):
#传入函数的图片先进行取反(255-原像素值)
#使用高斯函数滤波进行阈值选取
binary = cv.adaptiveThreshold(~img, 255, cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv.THRESH_BINARY, 11, -5)#dst选择默认值为None
return binary
#识别横线和竖线
'''
形态学腐蚀:
使用模版在图像上移动,如果发现有像素等于目标图像,就将其模板中心原点位置置为1
'''
def spot(img):
#腐蚀算法的色块大小,一般用长和宽的平方根为基数效果最好
rows, cols = img.shape
col_k = int(math.sqrt(cols) * 1.2) #宽
row_k = int(math.sqrt(rows) * 1.2) #高
#通过基于图形学的腐蚀和膨胀操作识别横线
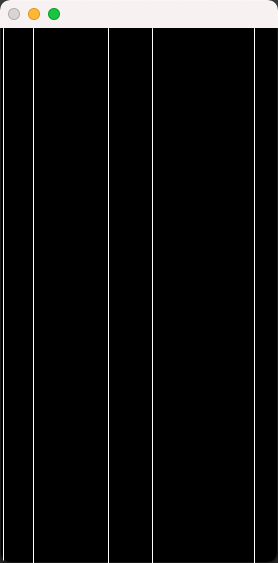
horizontal_line = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (col_k, 1)) #构造一个类似于横线的方形结构元素
eroded_col = cv.erode(img, horizontal_line, iterations=1) #使用横线模版进行腐蚀
dilatedcol = cv.dilate(eroded_col, horizontal_line, iterations=1)
#cv_show("识别的横线", dilatedcol)
#通过腐蚀识别竖线
vertical_line = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (1, row_k)) #构造一个类似于竖线的方块结构元素
eroded_row = cv.erode(img, vertical_line, iterations=1) #使用竖线模板进行腐蚀
dilatedrow = cv.dilate(eroded_row, vertical_line, iterations=1)
#cv_show("识别的竖线", dilatedrow)
#识别横线竖线的交点
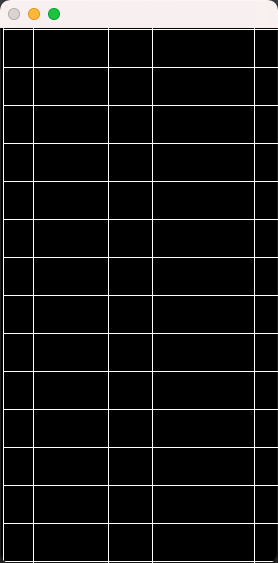
bitwiseAnd = cv.bitwise_and(dilatedcol, dilatedrow)
#识别表格:将横线图片和竖线图片相加
table = dilatedcol + dilatedrow
#cv_show("表格图片", table)
return bitwiseAnd, table
#存储横线和竖线的交点
def side_point(img):
list_x = []
list_y = []
x, y = img.shape
index = 0
for i in range(x):
for j in range(y):
if img[i][j] == 255:
#通过打印结果得到,一个交点刚好只占一个像素(如果交点过大,需要进行过滤)
if index != 0:
if i == list_x[-1] and j - list_y[-1] < 10:
continue
if index != 0:
if i != list_x[-1] and i - list_x[-1] < 10:
continue
list_x.append(i)
list_y.append(j)
index += 1
return list_x, list_y
#根据交点的位置对表格图片进行分割
def split_table(list_x, list_y, img):
index = 0
y = 0
ROI = []
for i in range(len(list_x) - 1):
if list_x[i] == 1 or list_x[i] == 0:
continue
if list_x[i] == list_x[i + 1]:
if index == 0:
ROI.append(img[0: list_x[i], list_y[i]: list_y[i + 1]])
else:
if y == 0:
temp = list_x[i - 1]
ROI.append(img[temp: list_x[i], list_y[i]: list_y[i + 1]])
y += 1
else:
y = 0
index += 1
return ROI
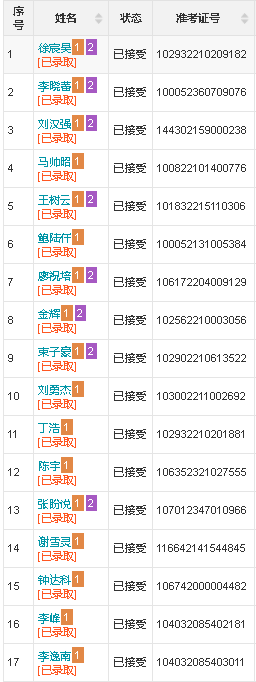
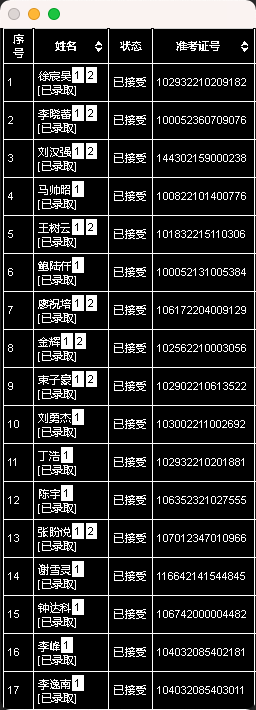
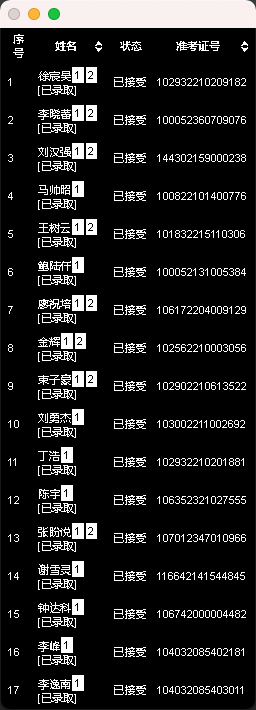
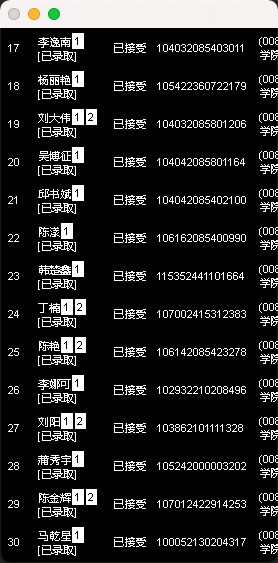
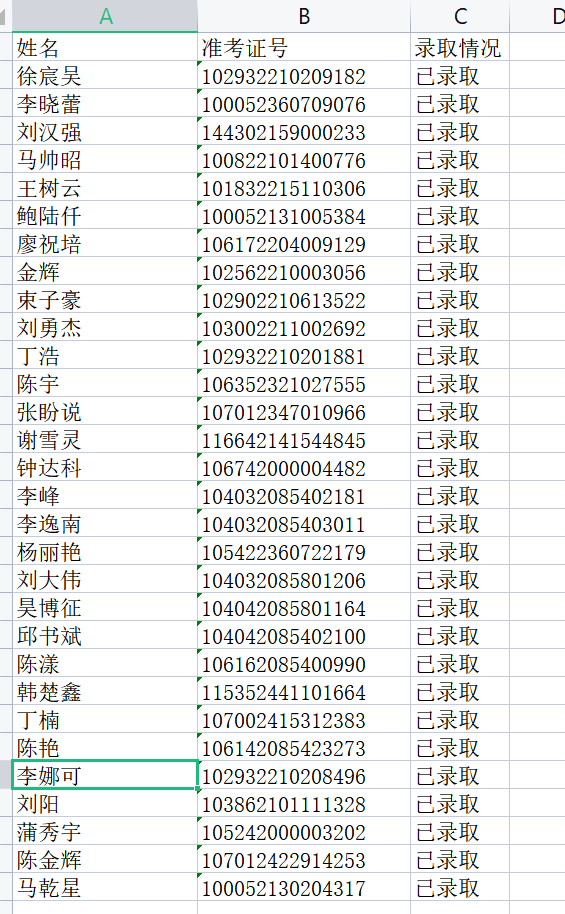
#文字识别(第一张图,带字段)
def ocr1(img_list):
from cnocr import CnOcr # 中文文字识别
cn_ocr = CnOcr()
import pytesseract # OCR英文文字识别库(数字)
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r'C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe'
name_list = []
number_list = []
admit_list = []
for i in range(0, len(img_list) - 1, 4): #步长为4的循环
index = 0
if i < 4: #直接将第一行信息跳过
continue
x, y = img_list[i + 1].shape
x1, y1 = img_list[i + 3].shape
img1 = img_list[i + 1][0: x // 2, 0: y // 2]
img2 = img_list[i + 1][x // 2: , 0: y // 2]
img3 = img_list[i + 3][10 : x1 - 10, :]
temp1 = cn_ocr.ocr(img1) #对应第二栏的信息上半部分(名字为2个字还得另外筛选)
temp2 = cn_ocr.ocr(img2) #对应第二栏信息下半部分
number_el = pytesseract.image_to_string(img3, lang='eng') #对应第四栏的信息
number = ""
for x in number_el:
if x >= '0' and x <= '9':
number += x
#print(temp1)
#print(number)
#print(temp2)
#对名字信息进行处理
for temp in temp1:
for j in range(len(temp)):
if j == 0:
name = ""
for y in temp[j]:
if y.isdigit(): #为数字字符串则跳过
continue
name += y
name_list.append(name)
#放入准考证号信息
number_list.append(str(number))
#填入录取信息
for temp in temp2:
for j in range(len(temp)):
if j == 0:
admit_information = ""
for y in temp[j]:
if y == '[':
continue
admit_information += y
admit_list.append(admit_information)
index += 1
return name_list, number_list, admit_list
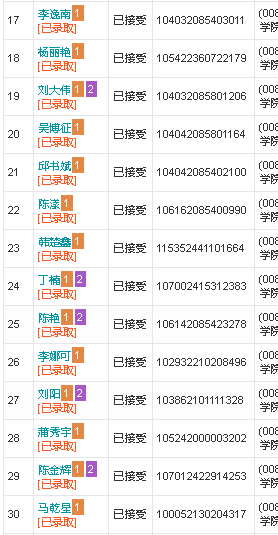
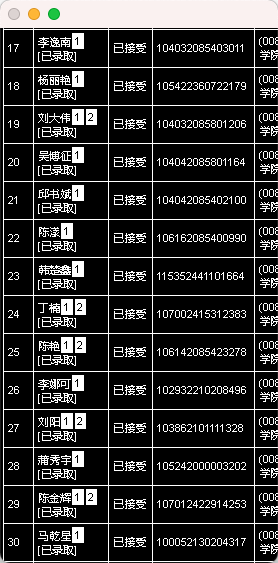
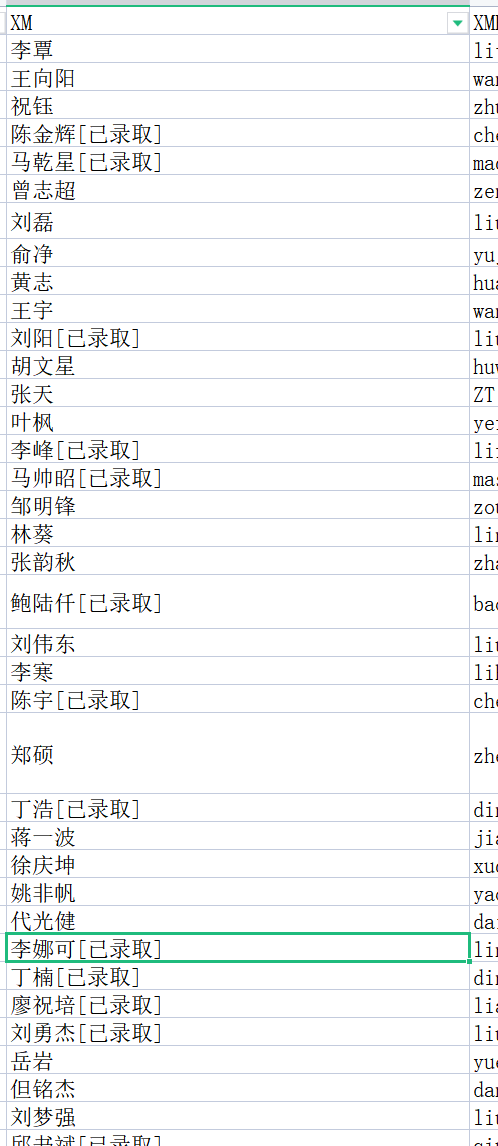
#文字识别(第二张图)
def ocr2(img_list):
from cnocr import CnOcr # 中文文字识别
cn_ocr = CnOcr()
import pytesseract # OCR英文文字识别库(数字)
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r'C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe'
name_list = []
number_list = []
admit_list = []
for i in range(0, len(img_list) - 1, 3): #步长为3的循环
index = 0
x, y = img_list[i].shape
x1, y1 = img_list[i + 2].shape
img1 = img_list[i][0: x // 2, 0: y // 2]
img2 = img_list[i][x // 2: , 0: y // 2]
img3 = img_list[i][10 : x1 - 10, :]
temp1 = cn_ocr.ocr(img1) #对应第二栏的信息上半部分(名字为2个字还得另外筛选)
temp2 = cn_ocr.ocr(img2) #对应第二栏信息下半部分
number_el = pytesseract.image_to_string(img3, lang='eng') #对应第三栏的信息
number = ""
for x in number_el:
if x >= '0' and x <= '9':
number += x
#print(temp1)
#print(number)
#print(temp2)
#对名字信息进行处理
for temp in temp1:
for j in range(len(temp)):
if j == 0:
name = ""
for y in temp[j]:
if y.isdigit(): #为数字字符串则跳过
continue
name += y
name_list.append(name)
#放入准考证号信息
number_list.append(str(number))
#填入录取信息
for temp in temp2:
for j in range(len(temp)):
if j == 0:
admit_information = ""
for y in temp[j]:
if y == '[':
continue
admit_information += y
admit_list.append(admit_information)
index += 1
return name_list, number_list, admit_list
#添加数据(考虑多次添加的情况)
def edit_exTable(table_name, sheet_name, list1, list2, list3):
workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook(table_name)
sheet = workbook[sheet_name]
#定位到新空白的单元格中(计算偏移量)
offset1 = 0
offset2 = 0
for i in range(1000):
if sheet.cell(i + 1, 1).value != None:
offset1 += 1
else:
break
for i in range(len(list1)):
if sheet.cell(1, 1).value != None:
if sheet.cell(i + offset1, 1).value == list1[i]: #防止上一次的图片末尾和新的图片头部有重复
offset2 += 1
continue
sheet.cell(i + 1 + offset1 - offset2, 1).value = list1[i]
sheet.cell(i + 1 + offset1 - offset2, 2).value = list2[i]
sheet.cell(i + 1 + offset1 - offset2, 3).value = list3[i]
workbook.save(table_name)
workbook.close()
#在已有表格中标注并增加已录取(身份证在第9栏,名字在第7栏)
def mark_exTable(table_name, sheet_name, list1, list2, list3):
workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook(table_name)
sheet = workbook[sheet_name]
for i in range(len(list1)):
for j in range(1000):
if sheet.cell(j + 1, 9).value == list3[i]: #找到身份证相等的情况
sheet.cell(j + 1, 7).value = list1[i] + "[" + list2[i] + "]"
break
workbook.save(table_name)
workbook.close()
# 显示图像
def cv_show(name, img):
cv.imshow(name, img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
def main():
#采集灰度图片
img1 = cv.imread("1.png", 0)
img2 = cv.imread("2.png", 0)
#cv_show("第一张图", img1)
#cv_show("第二张图", img2)
#图像二值化
binary1 = binary_img(img1)
binary2 = binary_img(img2)
#cv_show("二值化后的图1",binary1)
#cv_show("二值化后的图2", binary2)
#横线竖线交点图片识别和表格识别
intersection_img1, table1 = spot(binary1)
intersection_img2, table2 = spot(binary2)
cv_show("交点图片1", intersection_img1)
cv_show("交点图片2", intersection_img2)
print(intersection_img1)
#进行减法运算,提取纯文字图片
character_img1 = binary1 - table1
character_img2 = binary2 - table2
cv_show("纯文字图片1", character_img1)
cv_show("纯文字图片2", character_img2)
#通过交点图片提取出交点像素
myList_x1, myList_y1 = side_point(intersection_img1) #x代表行,y代表列
myList_x2, myList_y2 = side_point(intersection_img2)
# print(myList_x1)
# print(myList_y1)
# print(myList_x2)
# print(myList_y2)
#根据交点位置分割表格
img_list1 = split_table(myList_x1, myList_y1, character_img1)
img_list2 = split_table(myList_x2, myList_y2, character_img2)
#分割图片效果检测
# for img in img_list1:
# cv_show("", img)
# for img in img_list2:
# cv_show("", img)
#对分割好的图片进行文字识别
name_text1, number_text1, admit_text1 = ocr1(img_list1)
name_text2, number_text2, admit_text2 = ocr2(img_list2)
# print(name_text1)
# print(admit_text1)
# print(name_text2)
# print(admit_text2)
#新建表格并保存名字
workbook = openpyxl.Workbook()
workbook.create_sheet('录取情况')
sheet = workbook['录取情况']
sheet.cell(1, 1).value = '姓名'
sheet.cell(1, 2).value = '准考证号'
sheet.cell(1, 3).value = '录取情况'
workbook.save(u'接收复试同学已录取情况.xlsx')
#编辑表格并输入信息
edit_exTable(u'接收复试同学已录取情况.xlsx', '录取情况', name_text1, number_text1, admit_text1)
edit_exTable(u'接收复试同学已录取情况.xlsx', '录取情况', name_text2, number_text2, admit_text2)
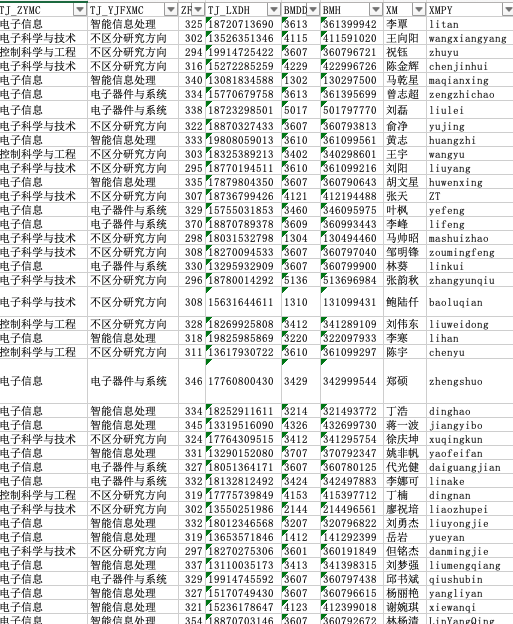
#在已有表格中查找并进行标注(通过身份证号查找)
mark_exTable(u'接收复试通知名单_副本.xlsx', 'YZ_SYTJ_SBMCJ_085046761', name_text1, number_text1, admit_text1)
mark_exTable(u'接收复试通知名单_副本.xlsx', 'YZ_SYTJ_SBMCJ_085046761', name_text2, number_text2, admit_text2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|